Photosynthesis Vs. Cellular Respiration
What is photosynthesis?
The process of using the energy in sunlight to make food (glucose). Is it really as simple as that? Of course not. As you have seen, photosynthesis includes many steps all conveniently condensed into one simple equation. In the five concepts describing photosynthesis, this process has been presented in an introductory fashion. Obviously, much more details could have been included, though those are beyond the scope of these concepts.
Photosynthesis
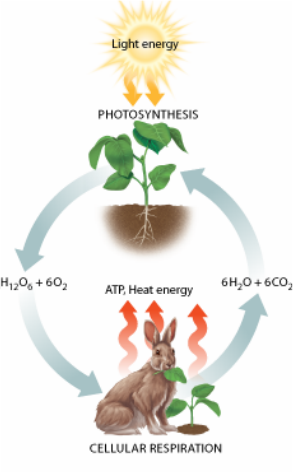
Photosynthesis vs. Cellular Respiration. What is Difference between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration? In the case of plants, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are reactions that complement each other. In fact it could be said that in both cases it is the same process, but in the opposite direction.
Summary
The following 10 points summarize photosynthesis.
- 6CO2 + 6H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
- Autotrophs store chemical energy in carbohydrate food molecules they build themselves. Most autotrophs make their 'food' through photosynthesis using the energy of the sun.
- Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast, an organelle specific to plant cells.
- The light reactions of photosynthesis occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast.
- Electron carrier molecules are arranged in electron transport chains that produce ATP and NADPH, which temporarily store chemical energy.
- The light reactions capture energy from sunlight, which they change to chemical energy that is stored in molecules of NADPH and ATP.
- The light reactions also release oxygen gas as a waste product.
- The reactions of the Calvin cycle add carbon (from carbon dioxide in the atmosphere) to a simple five-carbon molecule called RuBP.
- The Calvin cycle reactions use chemical energy from NADPH and ATP that were produced in the light reactions.
- The final product of the Calvin cycle is glucose.
FAQs
- What is photosynthesis?
The process of using the energy in sunlight to make food (glucose). But of course it is much more complex than that simple statement. Photosynthesis is a multistep biochemical pathway that uses the energy in sunlight to fix carbon dioxide, transferring the energy into carbohydrates, and releasing oxygen in the process.
- What is NADPH?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, an energy carrier molecule produced in the light reactions of photosynthesis. NADPH is the reduced form of the electron acceptor NADP+. At the end of the light reactions, the energy from sunlight is transferred to NADP+, producing NADPH. This energy in NADPH is then used in the Calvin cycle.
- Where do the protons used in the light reactions come from?
The protons used in the light reactions come from photolysis, the splitting of water, in which H2O molecules are broken into hydrogen ions, electrons, and oxygen atoms. In addition, the energy from sunlight is used to pump protons into the thylakoid lumen during the first electron transport chain, forming a chemiosmotic gradient.
- How do you distinguish between the Calvin cycle and the Krebs cycle?
The Calvin cycle is part of the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis. The Calvin cycle uses ATP and NADPH. The Krebs cycle is part of cellular respiration. This cycle makes ATP and NAPH.
- Do photosynthesis and cellular respiration occur at the same time in a plant?
Yes. Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts, whereas cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria. Photosynthesis makes glucose and oxygen, which are then used as the starting products for cellular respiration. Cellular respiration makes carbon dioxide and water (and ATP), which are the starting products (together with sunlight) for photosynthesis.
HTML Password Lock 5.3 Full Description Password protect html pages, web pages and whole web site. Based on strong algorithms, it will thoroughly encrypt your entire page so that no one can getting in unless he know the correct password. And the encrypted web page can work anywhere even without a web server. The HTML Password Lock is the tool for you. The HTML Password Lock is special software that will help you protect your web and HTML pages by adding passwords. There are a lot of hackers out there that might get important files and documents to copy your website so this program will protect your website with string algorithms. HTML Password Lock Password Protect Web pages and HTML pages in just a few clicks! With an easy-to-use wizard, you can password protect your Web pages with strong algorithms step-by-step in just a few clicks. Sean Curley, Denver, CO (USA) I purchased HTML password lock after looking at between 5 and 10 competing products. I am a novice web developer, but needed the ability to control access to my website by viewer's state location (due to professional licensing requirements) and also to have separate client-only access control for certain pages. Mtop html password lock 5.3.
Common Misconceptions
- A common student misconception is that plants photosynthesize only during daylight and conduct cellular respiration only at night. Some teaching literature even states this. Though it is true the light reactions can only occur when the sun is out, cellular respiration occurs continuously in plants, not just at night.
- The “dark reactions” of photosynthesis are a misnomer that often leads students to believe that photosynthetic carbon fixation occurs at night. This is not true. It is preferable to use the term Calvin cycle or light-independent reactions instead of dark reactions.
- Though the final product of photosynthesis is glucose, the glucose is conveniently stored as starch. Starch is approximated as (C6H10O5)n, where n is in the thousands. Starch is formed by the condensation of thousands of glucose molecules.
Explore More
Use this resource to answer the questions that follow.
- Avoid Misconceptions When Teaching About Plants at http://www.actionbioscience.org/education/hershey.html
- Why is it more appropriate to say chloroplasts, rather than chlorophyll, are necessary for photosynthesis?
- Why is much more than six water molecules necessary for photosynthesis?
- Do plants absorb any green light? Explain your answer.